Health is wealth! The phrase takes on a new meaning and importance during pregnancy. A pregnant person doesn’t just have to keep themselves healthy, but also the unborn baby.
This all comes with a lot of pressure and often some extra worry. Adversely, this new responsibility for expectant mums allows brands to market “miracle” or “must have” supplements and remedies to expectant mums – who naturally are keen to do everything to ensure the baby arrives happily and healthily.
So what about magnesium? Is magnesium really so important during pregnancy?
And if so, what type of magnesium should you take? Is it possible to take too much magnesium when pregnant?
Here’s our complete guide to everything you need to know about magnesium in pregnancy, including
- Benefits of magnesium during pregnancy
- Potential side effects of magnesium in pregnancy
- How to use magnesium safely during pregnancy
In this guide:
Can you take magnesium while pregnant?
The short answer is yes! Pregnant people can absolutely take magnesium supplements. In fact, in many cases, it’s recommended.
Hormonal changes can make pregnant people more susceptible to magnesium deficiencies, resulting in complications for mum and baby.
Mothers, on average, lose 20-25% of their magnesium in pregnancy, as it is excreted through the kidneys. And with both mum and foetus requiring the mineral, it’s often essential for magnesium to be replaced via a supplement.
When researchers looked at the average levels of natural magnesium consumption in pregnant women (through food sources as opposed to supplements), one study found that the mean intake of pregnant women was between 35% and 58% of the recommended dietary allowance (noted here as 450mg).
Notably, low-income women consumed 97-100 mg of magnesium for every thousand calories, while women with higher incomes averaged 120 mg per thousand calories.
As explained in a study covering the role of magnesium in pregnancy and fetal programming of adult diseases:
“Pregnant women are at higher risk of developing magnesium deficiency, with maternal, fetal, and pediatric consequences.
“A magnesium deficiency status during gestation may interfere with fetal growth and development and may favour premature labour.”
So, not only can magnesium deficiency in pregnant mothers lead to birth complications and health problems for the baby, but there is also the potential for long-term impact on human pathology in adulthood.
In short, if a mother is deficient in magnesium, the unborn baby is more likely to develop health conditions later in life.


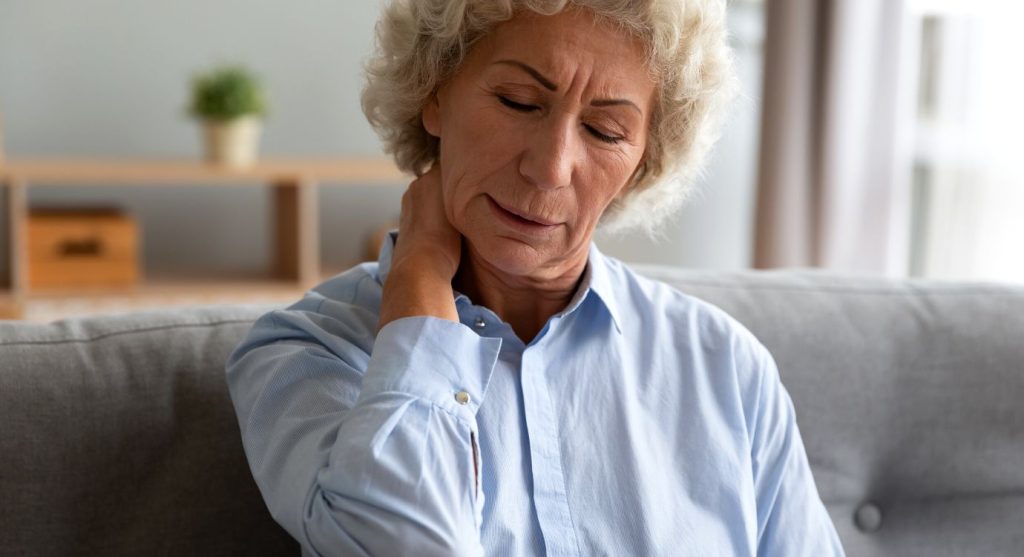
What are the symptoms of low magnesium in pregnancy?
Low magnesium in pregnancy can manifest in several unpleasant symptoms. These include
- Headaches
- Leg cramps
- Anxiety and depression
- High blood pressure
- Constipation.
- Nausea and vomiting
- High blood pressure
If pregnant people are experiencing other pregnancy-related symptoms – for example, morning sickness, which might present as nausea or vomiting – it might be difficult to spot signs of magnesium deficiency.
The two are connected somehow, as fluctuating hormones can alter magnesium levels and lead to morning sickness.
Magnesium plays a vital role in balancing cortisol, the primary hormone influencing a regulating blood sugar. Changes in blood sugar levels are thought to cause what we know as morning sickness (pregnancy nausea).
10% off on your first order
Complete this one-minute quiz and find the right products for you.
What are the benefits of magnesium during pregnancy?
There are many benefits to taking magnesium during pregnancy. Let’s take a look:
Reduced discomfort in pregnancy
Leg cramps at night, restless leg syndrome, headaches, difficulty sleeping (including insomnia), and constipation are all common symptoms women experience when pregnant. Luckily, they’re all symptoms that can often be alleviated by supplementing magnesium (in the case of a deficiency).
Read more: Magnesium for sleep
Supporting emotions
Pregnancy, and the postpartum period, can be an emotional rollercoaster. Even if you are incredibly excited to give birth and have your baby, it’s normal for pregnant women to feel vulnerable and anxious.
Hormonal changes in pregnancy often manifest in being over-emotional, irritable and teary, while sickness and tiredness can often contribute to low mood.
While the mineral hasn’t been studied specifically in supporting emotions in pregnant people, magnesium is thought to help with depression and anxiety more generally.
In one clinical trial, researchers looked at the effect of magnesium supplementation on depression.
The study found that supplementing 248 mg of magnesium daily led to participants reporting a significant difference in the amount and severity of depression and anxiety symptoms compared to participants who received a placebo.
Two other papers reported improved depressive symptoms after magnesium intake compared to controls.
Reduced risk of complications
One study found pregnant women with low serum magnesium levels were more likely to go into preterm labour or have a preterm birth than women with adequate magnesium levels.
Women who take magnesium throughout their pregnancy are also thought to be less likely to develop high blood pressure, uterine irritability, preeclampsia, or eclampsia.
One study looked at the effect of magnesium supplementation on pregnancy outcomes and found that in all pregnancy outcomes, the group that received magnesium with a multi-mineral supplement experienced fewer pregnancy complications than the two control groups.


What are the side effects of magnesium during pregnancy?
Magnesium is a safe and effective supplement that most people can slot into health and wellness routines without an issue.
However, some people might experience side effects when taking magnesium, especially if they consume excess (more than a recommended daily dose).
These symptoms might include vomiting, nausea, diarrhoea, urine retention, and lethargy.
How much magnesium is safe during pregnancy?
So, how much magnesium is safe to take during pregnancy? Should pregnant people take more or less magnesium than an ‘average’ dose for size, age, and gender?
As a rule, the recommended daily dose of magnesium during pregnancy is 350-360 milligrams. This magnesium level will help replace a mother’s depleted magnesium levels while avoiding complications. Note that 500mg per day is considered to be too high an amount for a pregnant person.
Do also note that the UK government drug safety guidelines state that maternal administration of magnesium sulfate for longer than 5–7 days in pregnancy may be associated with adverse effects in the foetus.
These include hypocalcaemia, skeletal demineralisation, osteopenia, and other adverse skeletal effects. As such, it’s important to approach any magnesium supplementation of care and speak with a medical professional about the best amount and type of magnesium to take to support a pregnancy safely.
However, also note that this warning is supported by a study conducted in Taiwan. But crucially, it focused on magnesium sulfate injections given in a medical setting during pregnancy. As such, these findings shouldn’t be extrapolated or applied as a concern about the type of daily supplementation discussed in this article.
Note that magnesium is also safe to take while breastfeeding, so new mums can continue supplementation even after the baby is born.


What happens if you have too much magnesium during pregnancy?
As explained above, excessive magnesium sulfate during pregnancy may lead to adverse effects, so health professionals must monitor injections carefully. More broadly, expectant mothers consuming too much magnesium might also lead to the side effects described above as the body attempts to eliminate excess magnesium in the system.
Always stick to recommended dosage guidelines and check in regularly with a health professional during pregnancy. They can monitor magnesium levels and advise on a safe and supportive dosage for both mother and baby.
Read more: How long does magnesium stay in your body
Final words on magnesium in pregnancy
In summary, supplementing magnesium can help expectant mums remain healthy and ensure their baby isn’t leaving them without the essential magnesium for themselves.
Prenatal nourishment is super important for the health of mum and baby, and including daily magnesium supplements can improve pregnancy experiences (reducing symptoms such as headaches, leg cramps, and sleep trouble) while supporting a baby’s growth and development.
It’s also worth noting, for people trying to become pregnant or expecting to want to become pregnant in the near future, that studies support the notions that women who start taking a magnesium supplement before pregnancy might experience fewer side effects during pregnancy, such as like morning sickness in the first trimester.